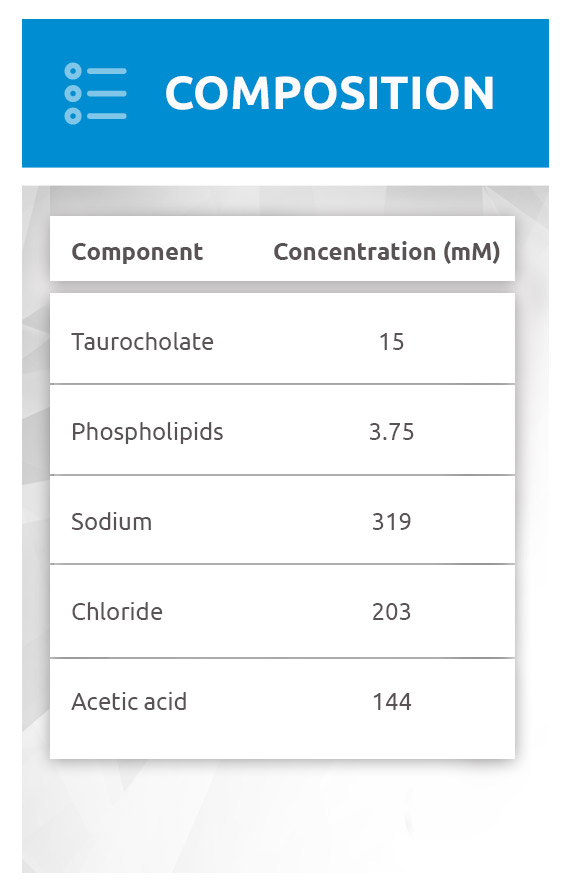
What is the composition of FeSSIF?
What's the composition of FeSSIF?
In response to eating a meal, the upper intestines secrete surfactants (bile salt and phospholipid) to help break the food down. FeSSIF contains the same types and levels of these surfactants. These are critical, particularly for poorly water-soluble drugs, because they form mixed micelles which can enhance drug solubility and dissolution greatly. This in turn can have a significant effect on how the drug is absorbed. It’s one of the reasons why absorption of lipophilic poorly-soluble drugs is often influenced by food. FeSSIF has the average pH of fed intestinal fluid and similar osmolarity (about 670 mOsmol/L) too. These are important parameters to control when testing drug products or formulations sensitive to pH and salt content.

FeSSIF (Fed State Simulated Intestinal Fluid) is a very useful drug development tool. Tests in this dissolution medium can help reveal how your oral drug is likely to dissolve and potentially be absorbed in fluid from the upper intestine after eating a meal.
The stability, solubility and dissolution data you generate from testing in FeSSIF can help identify critical factors influencing your drug’s absorption in the fed state. This is especially important for water insoluble drugs. These results also support your selection of the appropriate solid state and formulation approach for your drug. Experiments are performed using standard laboratory equipment (such as USP Dissolution Apparatus 1 or 2). Drug content is analysed using HPLC.


















 Home
Home















