What are Intestinal fluid, simulated, TS and USP-SIF (sp)?
Intestinal fluid, simulated, TS (Test Solution) is a simple buffer used for dissolution testing containing pancreatin. It is described in the Test Solution section in the United States Pharmacopeia. The abbreviation USP-SIF (sp) refers to the test solution without pancreatin, where "sp" stands for sine pancreatin. It was one of the original dissolution media used to simulate the pH of the intestinal tract but is just a buffer and not classed as a biorelevant medium because it lacks the essential physiological surfactants present in the gastrointestinal tract.
USP-SIF (sp) – is a phosphate buffer containing a higher concentration of potassium ions compared to sodium.
The buffer has a pH of 6.8, with an osmolarity of approximately 110mOsmol/kg and buffer capacity around 18.5mEq/L/pH unit.
USP-SIF (sp) is NOT FaSSIF medium
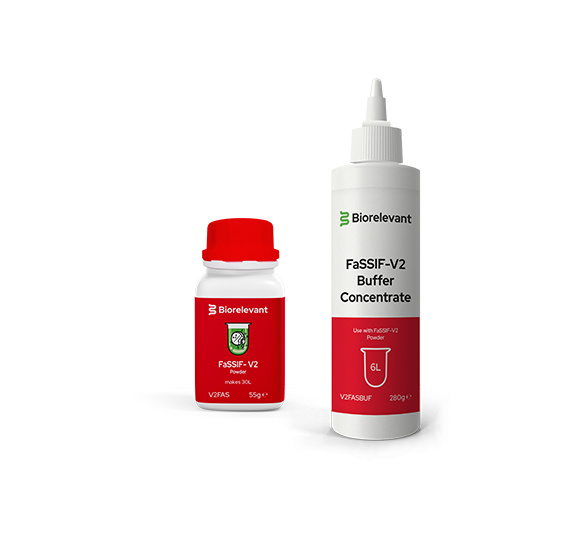
This standard USP-SIF (sp) buffer differs significantly from biorelevant FaSSIF medium and the biorelevant FaSSIF buffer used for the preparation of FaSSIF.
• FaSSIF biorelevant medium contains surfactants that mimic the gastrointestinal environment in the fasted state. These surfactants are crucial for testing drug products with poorly soluble drugs because they aid in wetting and solubilization. These surfactants are NOT present in USP-SIF (sp).
• FaSSIF biorelevant buffer is used to prepare FaSSIF (with the addition of 3F Powder®). FaSSIF biorelevant buffer is designed to simulate the aqueous environment (in terms of buffer capacity and osmolarity) of fasted state intestinal fluid more closely than USP-SIF (sp). USP-SIF (sp) has a much higher buffer capacity and does not contain sodium chloride to adjust the osmolarity to an oral physiological level.
















 Home
Home















